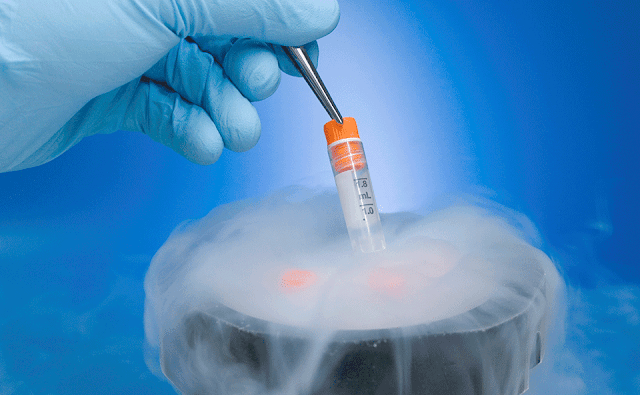
Sperm Freezing
Sperm freezing is the process of collecting, analyzing, freezing and storing a man’s sperm. These samples are used later for fertility treatments or for donation to other couples or individuals for artificial insemination, including same-sex female partners. The overall process is known as cryopreservation and is also called a sperm bank.
Cryopreservation process involves:
●
Routine screening for infection (HIV, hepatitis and
rapid plasma regain test for syphilis)
●
Provision of semen sample or sperm extraction if
required
●
Analysis of sperm quantity and quality
●
Freezing of viable sperm
●
Storage of the sperm indefinitely
The samples are separated into multiple vials to be frozen.
When the time comes, the sperm is thawed, washed and tested for mobility prior
to use in IUI or IVF. Donated sperm usually has to be stored for six months
first in order to screen the donor for infections.
You may wish for sperm freezing if:
●
You are affected by a condition,
or medical treatment for a condition that may affect your fertility.
●
You are about to have
a vasectomy and want sperm available in case your mind changes about having children.
●
Your sperm
quality is deteriorating.
●
Your profession
involves danger or staying away from your partner for prolonged periods e.g.
Armed forces overboard.
●
You are going through a transgender operation or a male transitioning to a female and would wish to
preserve your fertility for future use.
●
You may be growing old and increasing chances of
infertility
Treatment with frozen sperm is just as successful as
treatment using fresh sperm.
Stored or banked sperm can be frozen indefinitely until
needed for assisted reproductive procedures, such as IVF and IntrauterineInsemination (IUI) or sperm donation.
The primary benefits of freezing sperm are to allow a man to
preserve his fertility by using his sperm at a later date or to give an infertile couple, an infertile individual or a lesbian couple a chance to
conceive.
Risks involved in freezing sperm
No risks or side effects to collecting semen samples
naturally i.e. through masturbation. Discomfort and bleeding may result if a sperm sample is extracted through a surgical procedure.
Sperm freezing has been successfully used since 1953 to help
individuals conceive healthy babies. As the technology advanced the process has
also improved while being safe on its own.
The freezing and thawing might result in sperm not
surviving. But as semen ejaculations contain an appropriate number of sperm,
chances of having an appropriate number of healthy sperm during fertility
treatment are quite high. The surviving sperm cells can easily fertilize an
embryo and the chances are not jeopardized during the freezing or thawing
process.
Cryopreservation is considered to have no time limit, and
stored sperm as old as 20 years have been used to create healthy babies.
Success rates for having a baby through sperm freezing
The success rates using thawed sperm vary and depend on the quality of the sperm once it's thawed, as some sperm gets damaged during thawing. Sperm banking has produced thousands of babies but it doesn’t guarantee that you'll be able to father a child.
The following success rates are from the Human Fertilization
and Embryology Society and include healthy people having treatment using
insemination and IVF.
●
under 35 the success rate is around 25 births out of
100 treatments (25%)
●
aged 35 to 39 the success rate is between 15 and 20
births out of 100 treatments (15 to 20%)
●
aged 40 to 42 the success rate is between 10 and 15
births out of 100 treatments (10 to 15%)
The AustralianConcept Infertility Medical Center is at the fore-front of fertility technology, consistently recording high success rates, a substantial percentage of our cases have had positive results with more than 11,000 pregnancies Our programs address both male and female infertility problems with thoroughness.


Comments
Post a Comment